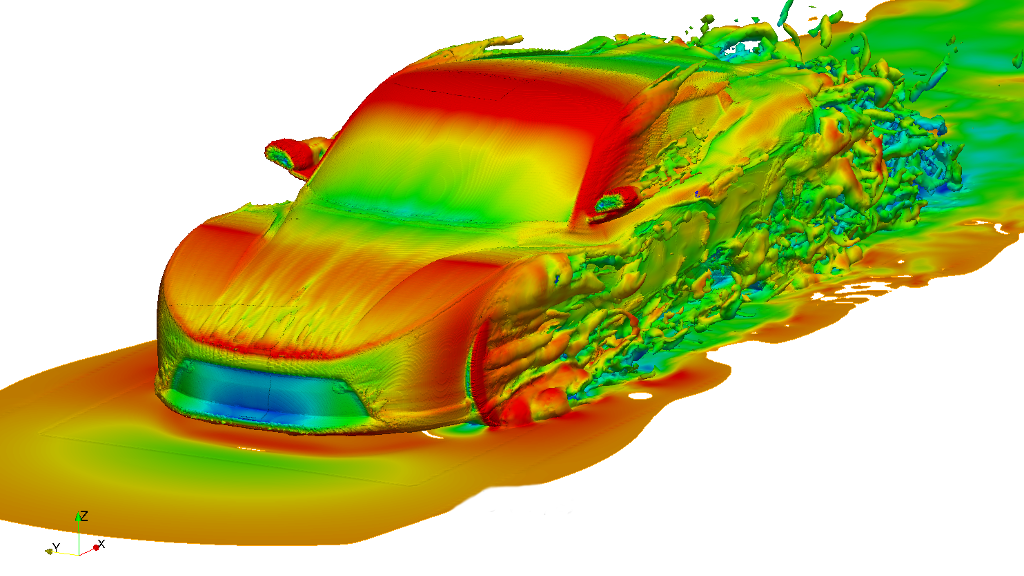
Have you ever wondered how engineers simulate and understand the complex behavior of fluids in various applications? Whether it’s designing efficient airplanes, optimizing car aerodynamics, or even predicting weather patterns, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) plays a pivotal role. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of CFD, exploring its fundamental principles, applications, and the impact it has on numerous industries.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that employs numerical methods, algorithms, and computer simulations to analyze and predict fluid flow behavior. It combines principles from mathematics, physics, and computer science to solve the governing equations that describe fluid flow phenomena.
The underlying equations for fluid flow, known as the Navier-Stokes equations, are incredibly complex and often impossible to solve analytically. CFD offers a powerful alternative by discretizing the fluid domain into a mesh of smaller elements, applying numerical methods to approximate the governing equations, and then solving them iteratively.
Applications of CFD:
Aerospace and Automotive Industries:
CFD has revolutionized the aerospace and automotive sectors by enabling engineers to optimize designs, reduce drag, enhance fuel efficiency, and improve performance. By simulating airflow around vehicles or aircraft, engineers can identify areas of high drag, turbulence, or pressure gradients, leading to informed design modifications.
Energy and Environmental Engineering:
CFD plays a crucial role in designing energy-efficient systems and assessing environmental impacts. It helps optimize wind turbine designs, evaluate heat transfer processes in power plants, model pollutant dispersion, and analyze ventilation systems in buildings. By simulating and understanding fluid behavior, engineers can make informed decisions to reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental impact.
Biomedical Engineering:
In the field of biomedical engineering, CFD aids in studying blood flow patterns, optimizing prosthetic devices, and designing drug delivery systems. It allows researchers to simulate the behavior of fluids within the human body, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, optimizing stent designs, and improving surgical techniques.
Weather Prediction and Climate Modeling:
CFD is instrumental in weather prediction and climate modeling by simulating atmospheric flows, ocean currents, and climate patterns. Sophisticated CFD models help meteorologists and climatologists predict severe weather events, understand climate change phenomena, and assess the impact of human activities on the environment.
Challenges and Advances in CFD:
While CFD has proven to be an invaluable tool, it does face certain challenges. Simulating complex fluid flow phenomena requires substantial computational resources and time. The accuracy of CFD simulations heavily relies on the quality of the underlying models, meshing techniques, and boundary conditions. Validating CFD results with experimental data is also essential to ensure reliability.
Recent advances in high-performance computing (HPC) and numerical methods have greatly enhanced the capabilities of CFD. With the advent of cloud computing and parallel processing, engineers can tackle larger and more complex simulations. Furthermore, improvements in turbulence modeling, adaptive meshing, and the integration of artificial intelligence techniques have contributed to more accurate and efficient CFD simulations.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has revolutionized the way engineers understand and analyze fluid flow phenomena. Its applications span across various industries, enabling optimization, innovation, and informed decision-making. As technology continues to advance, CFD will play an increasingly significant role in solving complex fluid flow problems, driving advancements in engineering, energy, healthcare, and environmental sustainability. The fascinating world of CFD is continuously evolving, offering endless possibilities for scientific exploration and practical applications.